These two powerful solutions often compete for attention: Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) and Marketing Automation Platforms (MAPs). But which one truly serves your business needs?
As businesses aim to enhance personalized experiences and operational efficiency, choosing between a Customer Data Platform (CDP) and a Marketing Automation Platform (MAP) is critical.
This guide will cover the main differences between CDPs and MAPs, aiding you in making a decision that aligns with your business needs.
Before diving deep into each solution, it’s important to understand that both CDPs and MAPs serve distinct purposes while sharing some overlapping functionality. As experts in integration solutions serving over 25,000 subscribers globally, we’ve helped countless organizations navigate this decision successfully.
Let’s explore how each platform can benefit your business and which might be the better fit for your specific needs.
Customer Data Platform vs Marketing Automation
The choice between a customer data platform (CDP) and a marketing automation platform (MAP) depends on your business’s goals and needs.
Ready to discover which solution aligns best with your business objectives? Let’s begin with a detailed look at Customer Data Platforms.
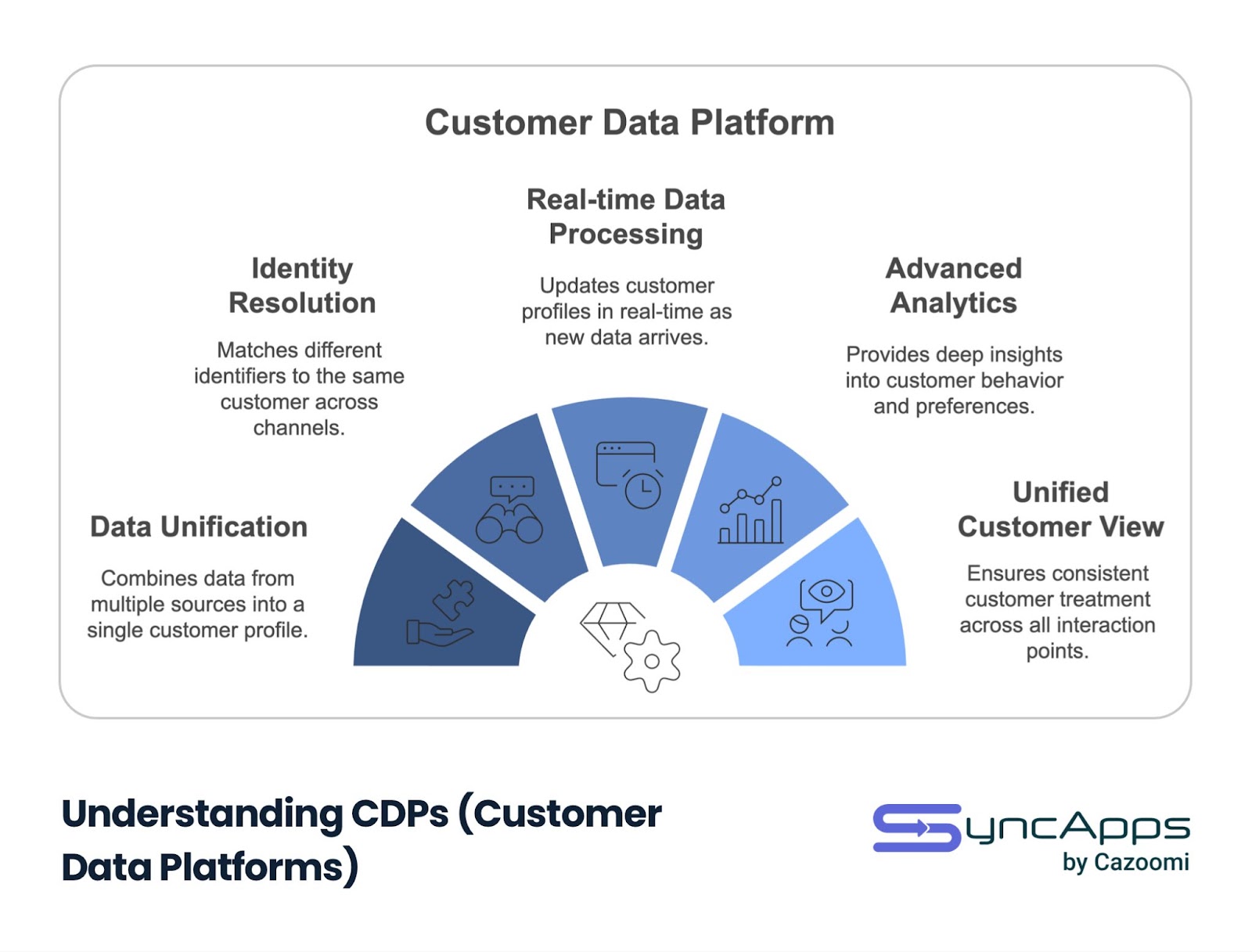
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is a unified database system that creates persistent, consistent customer records from multiple data sources. Unlike traditional data management solutions, CDPs are specifically designed to create a comprehensive, real-time view of each customer, enabling personalized experiences across all touchpoints.
CDPs excel at creating a single source of truth for customer data, making them invaluable for businesses focused on delivering personalized customer experiences. Here are the key features that define a CDP:
Data Unification
Combines customer data from multiple sources into a single, coherent customer profile
Identity Resolution
Matches different identifiers to the same customer across various channels and devices
Real-time Data Processing
Updates customer profiles in real-time as new data becomes available
Advanced Analytics
Provides deep insights into customer behavior and preferences
CDPs are designed to integrate with various systems and data sources, including:
CDPs are particularly valuable for businesses that:
A CDP is best for businesses that need to unify and analyze customer data from multiple channels to create personalized experiences.
For example, an e-commerce business might use a CDP to: Track customer behavior across web, mobile, and in-store channels Create personalized product recommendations Develop targeted marketing campaigns based on comprehensive customer profiles Measure and optimize customer lifetime value
Learn more about how to leverage customer data effectively in our guide on building amazing campaigns with customer data.
While CDPs offer powerful data management capabilities, they’re just one part of the marketing technology ecosystem. Understanding how they compare to Marketing Automation Platforms is crucial for making the right choice for your business.
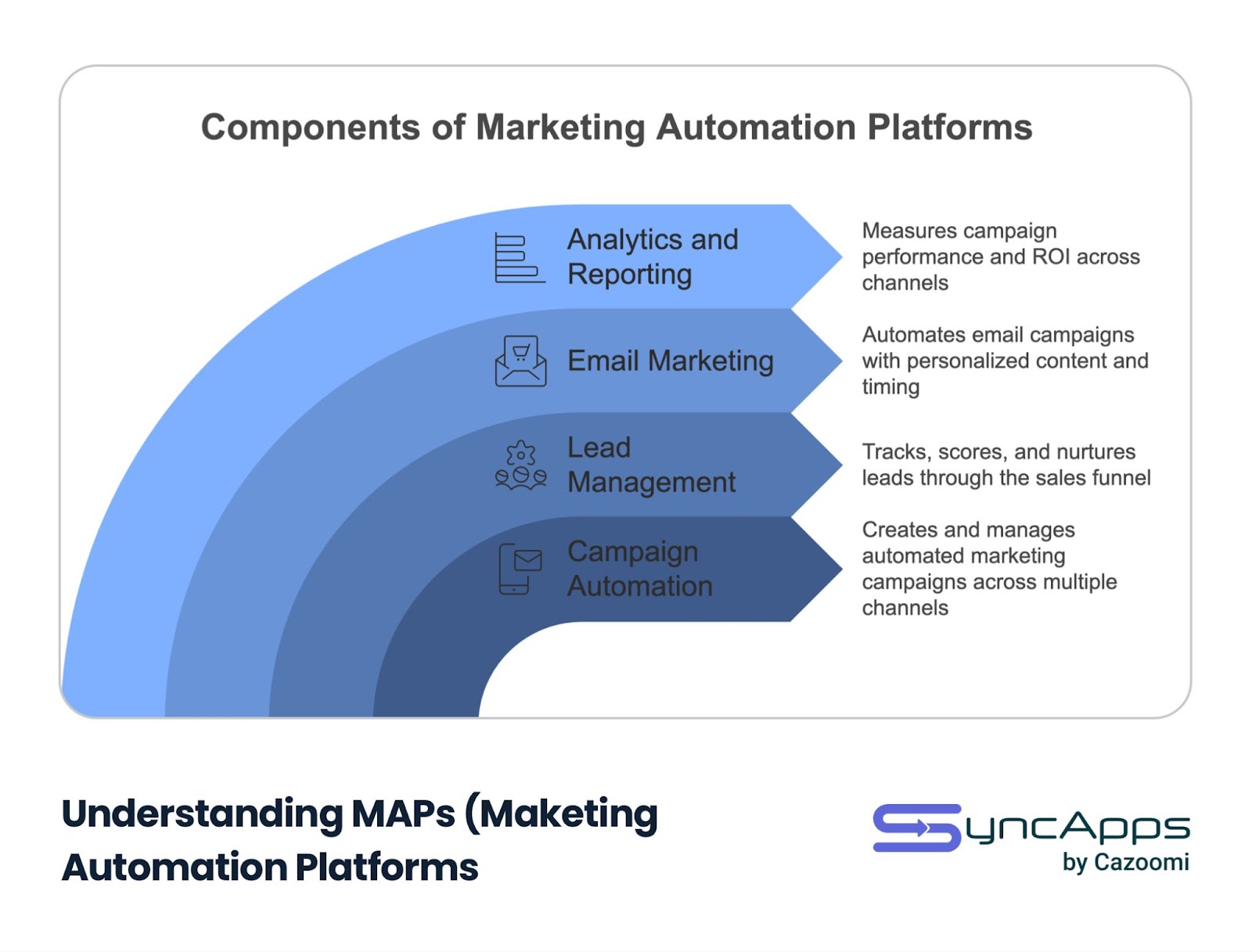
Marketing Automation Platforms (MAPs) are sophisticated software solutions designed to streamline and automate marketing tasks, making campaign management more efficient and effective. These platforms help businesses automate repetitive marketing activities while maintaining personalized customer communications at scale.
Marketing Automation Platforms excel at streamlining marketing operations and delivering targeted communications across multiple channels. Here’s a detailed look at their key features:
Campaign Automation
Creates and manages automated marketing campaigns across multiple channels
Lead Management
Tracks, scores, and nurtures leads through the sales funnel
Email Marketing
Automates email campaigns with personalized content and timing
Analytics and Reporting
Measures campaign performance and ROI across channels
| Benefit | Description | Impact |
| Time Efficiency | Automates repetitive marketing tasks | Frees up marketers for strategic activities |
| Consistent Communication | Maintains regular customer touchpoints | Improves customer engagement |
| Lead Nurturing | Automated follow-up sequences | Higher conversion rates |
| Performance Tracking | Comprehensive analytics | Better ROI measurement |
MAPs can automate various marketing tasks, including:
Modern MAPs typically integrate with:
Marketing Automation Platforms are particularly valuable for organizations that:
A MAP is best for businesses that want to automate marketing tasks and improve campaign management efficiency.
For example, a B2B company might use a MAP to: Automate lead nurturing sequences Schedule and manage social media campaigns Track campaign performance across channels Generate and distribute marketing reports
Discover more about maximizing your marketing automation potential in our guide on best practices of marketing automation.
While Marketing Automation Platforms offer powerful automation capabilities, understanding how they compare to CDPs is crucial for making an informed decision about which solution best fits your business needs.
For businesses considering marketing automation implementation, check out our detailed guide on how to assess your marketing automation needs.

Understanding the fundamental differences between Customer Data Platforms and Marketing Automation Platforms is crucial for making the right choice for your business. Let’s explore these differences across several key dimensions.
| Aspect | Customer Data Platform (CDP) | Marketing Automation Platform (MAP) |
| Primary Purpose | Unifying and analyzing customer data from multiple sources | Automating marketing tasks and campaign management |
| Data Handling | Creates persistent, unified customer profiles | Focuses on campaign execution and tracking |
| Main Strength | Customer data unification and insight generation | Marketing process automation and efficiency |
| Time Focus | Real-time data processing and updates | Scheduled and triggered activities |
The fundamental difference between CDPs and MAPs lies in their approach to data management:
CDP Integration Focus:
MAP Integration Focus:
The implementation requirements for CDPs and MAPs differ significantly:
| Consideration | CDP Implementation | MAP Implementation |
| Technical Complexity | Higher – requires data architecture planning | Moderate – focuses on workflow setup |
| Time to Value | Longer – comprehensive data integration needed | Shorter – can start with basic automation |
| Resource Requirements | Data engineers and analysts needed | Marketing team can handle most tasks |
| Maintenance Needs | Ongoing data quality management | Regular campaign optimization |
When evaluating the cost of each solution, consider:
For more insights on implementation considerations, check out our guide on enterprise integration requirements.
The choice between a CDP and MAP should align with your business’s primary objectives: data unification and analysis (CDP) or marketing task automation (MAP).
Understanding these differences is crucial, but making the right choice requires careful consideration of your specific business needs. Learn more about optimizing your marketing processes in our article about overcoming data silos and improving team collaboration.
Selecting between a Customer Data Platform and a Marketing Automation Platform requires careful consideration of your organization’s specific needs, capabilities, and goals. Let’s break down the key factors that should influence your decision.
Your organization’s size and operational complexity play a crucial role in determining which solution best fits your needs:
Different industries have varying needs when it comes to customer data and marketing automation:
| Industry | Recommended Solution | Key Reasons |
| E-commerce | CDP | Need for unified customer profiles across multiple channels |
| B2B Services | MAP | Focus on lead nurturing and campaign automation |
| Retail | CDP | Omnichannel customer experience management |
| SaaS | MAP | Emphasis on automated customer communications |
Use this framework to evaluate your needs:
Choose a CDP if you need:
Choose a MAP if you need:
Before making your final decision, consider these implementation factors:
Learn more about implementation strategies in our guide on successful integration implementation.
Consider these financial factors:
Remember: The right choice isn’t always about selecting the most feature-rich solution, but rather the one that best aligns with your business objectives and capabilities.
For more insights on maximizing your marketing technology investment, check out our article on why businesses need marketing automation.
Whether you choose a CDP or MAP, successful implementation requires careful planning and execution. This section outlines key practices to ensure a smooth implementation process and maximize your return on investment.
Before beginning implementation, ensure you have these essential elements in place:
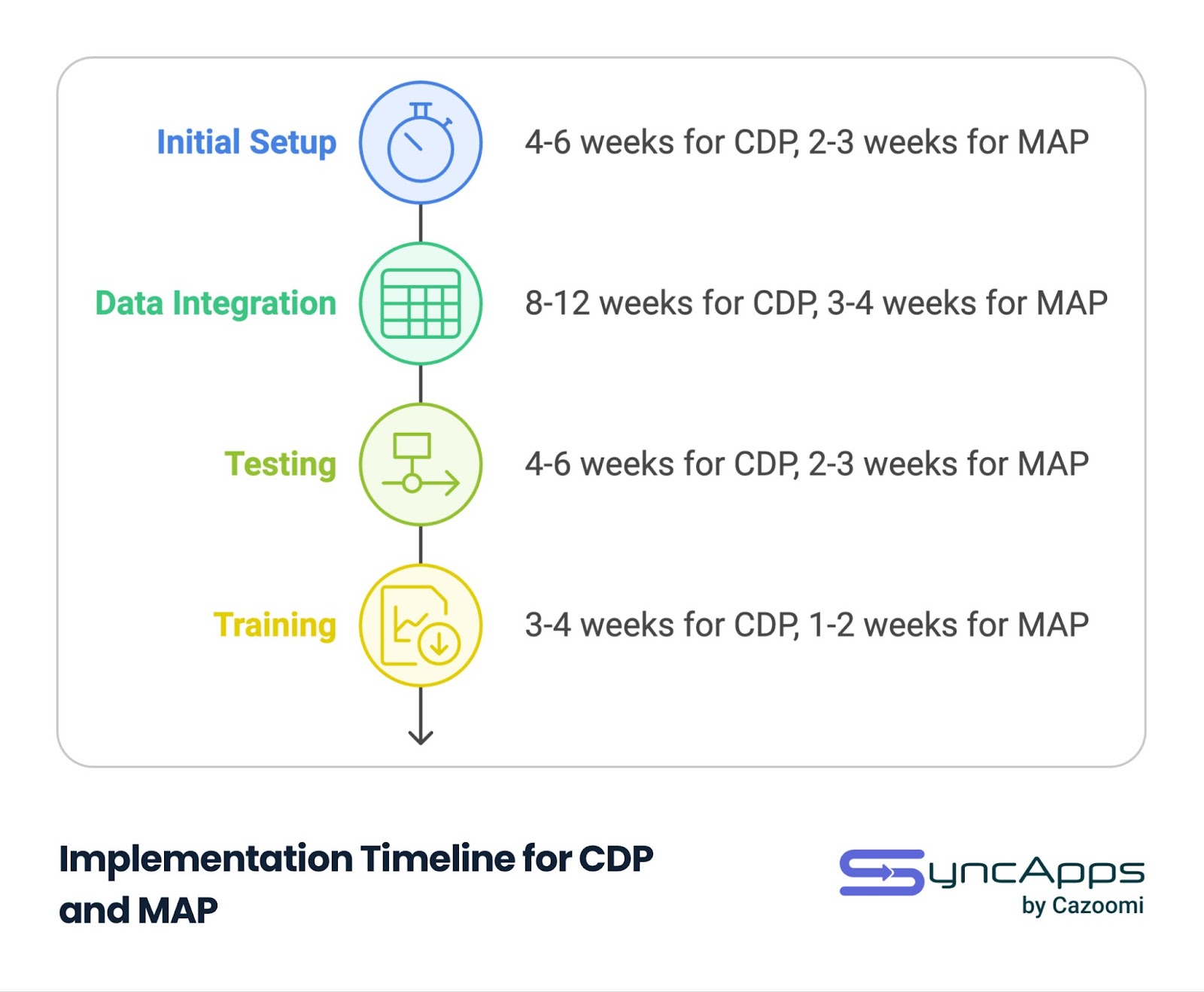
| Phase | CDP Timeline | MAP Timeline |
| Initial Setup | 4-6 weeks | 2-3 weeks |
| Data Integration | 8-12 weeks | 3-4 weeks |
| Testing | 4-6 weeks | 2-3 weeks |
| Training | 3-4 weeks | 1-2 weeks |
Data Quality Issues
Challenge: Inconsistent or incomplete data across systems
Solution:
Integration Complexity
Challenge: Difficulty connecting with existing systems
Solution:
User Adoption
Challenge: Resistance to new systems and processes
Solution:
Ensure you have these key resources available for successful implementation:
Track these key metrics to measure implementation success:
| Metric Category | CDP Metrics | MAP Metrics |
| Data Quality | Profile completeness, data accuracy | List quality, segmentation accuracy |
| System Performance | Data processing speed, integration success | Campaign execution time, automation reliability |
| User Adoption | Active users, feature utilization | Campaign creation rate, automation usage |
For more insights on successful implementation, check out our guide on requirements gathering for integration projects.
Remember: Successful implementation is not just about technical setup – it’s about ensuring the solution delivers real business value through proper planning, execution, and monitoring.
Learn more about maintaining system effectiveness in our article on ensuring data quality in the integration process.
The choice between a Customer Data Platform and a Marketing Automation Platform represents a significant decision for your organization’s future. Let’s recap the key considerations to help you move forward with confidence.
When choosing between a CDP and MAP, remember these essential points:
Consider these factors when making your final decision:
| Factor | Choose CDP If | Choose MAP If |
| Primary Goal | Data unification and analysis | Marketing automation and efficiency |
| Resources | Have technical team and budget | Limited technical resources |
| Timeline | Can invest in longer implementation | Need quick implementation |
| Data Needs | Complex data requirements | Basic data management needs |
Remember: The best choice is the one that aligns with your business objectives, resources, and long-term strategy.
To move forward with your decision:
For more guidance on implementing your chosen solution, explore our detailed guide on the benefits of early solution integration.
Whether you choose a CDP or MAP, success depends on careful planning, proper implementation, and ongoing optimization. The key is to select the solution that best fits your organization’s specific needs and capabilities. Both solutions offer valuable benefits, and in some cases, organizations may benefit from implementing both platforms to create a comprehensive marketing technology stack. The most important factor is ensuring that your choice aligns with your business objectives and provides the functionality you need to achieve your goals.
Ready to learn more about integration solutions? Discover how our platform can help you maximize the value of your chosen solution by reading about why integrations are essential for success.
Don’t let the complexity of choosing between a CDP and MAP hold you back. Take the first step toward improving your marketing technology stack:
Need help determining the right integration solution for your chosen platform? Contact our support team for expert guidance on maximizing your marketing technology investment.