
What is digital transformation and why is it that almost everyone seems to care about it?
Digital transformation is the process and strategy that involves the use of digital technology to bring a drastic change in business operations with a primary focus on customer service.
Since we live in an age of digitization, you will commonly hear the term digital transformation being thrown around every now and then. Understandably so, seeing that every company, irrespective of the line of business or size, is continuously increasing its reliance on data and technology.
The widespread acceptance of digitization is attributed to the desire by brands to enhance their efficiency, besides delivering value to their customers.
The History of Digital Transformation
One might think that the concept of digital transformation is as old as computer technology, but it really isn’t. The history of digital transformation can be traced to the 1990s. This is around the same time that mainstream internet hit the ground running.
Over time, digitization has become an essential part of our lives. It affects how we work, travel, shop, govern, educate and even how we live.
Digitization, however, is different from digital transformation. The former means moving from analog to digital. A few years ago, record-keeping involved a lot of paperwork. Whether the documents were typed or handwritten, business data was mostly analog.
The process of gathering or sharing information meant dealing with physical documents – photocopies, faxes, as well as papers and binders.
When computers became mainstream, a good number of businesses began converting all the handwritten or typed documents to digital computer files. That is what we refer to as digitization. Digitization made locating and sharing information immensely easier.
Sadly, there wasn’t much change when it came to the methods of using digital records by businesses. While digital data was significantly more efficient for organizations compared to analog data, the processes and systems remained pretty much the same.
They were mostly designed around the ideas from the analog era in aspects such as finding, sharing, and using information.
Unlike digital transformation, digitization doesn’t entail changing how business is done or the creation of new forms of business types. It only goes as far as making access to data faster and better – as opposed to when information is ditched in a dusty archive somewhere and when the thought of finding it makes you want to quit your job.
On the other hand, digital transformation has dramatically changed the way of doing business. In many instances, it has facilitated the creation of entirely new types of businesses.
Digital transformation practices are primarily used in the business context. The coming of digital technologies has triggered the development of new business models as well as revenue streams.
Both emerging technologies and foundational technologies have been instrumental in digital transformation. For instance, artificial intelligence, cloud computing and the Internet of Things are significant stimulants of transformation.
On the other hand, data management and analysis come in handy in the interpretation of vast volumes of data generated by digital transformation.
There is one thing we mustn’t forget, though. Digital transformation doesn’t only revolve around technology. Instead, it happens when people, businesses and technology intersect with a broader business strategy acting as the guide.
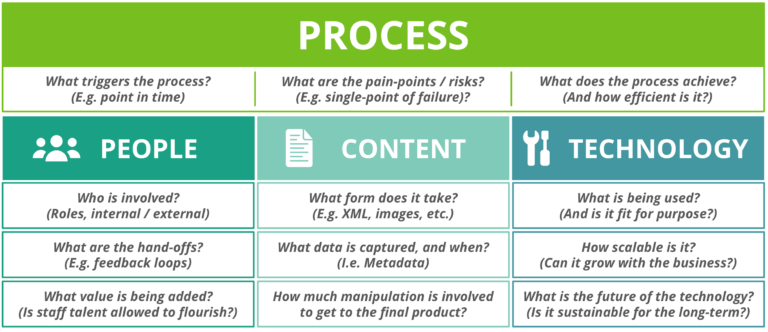
Image Source: Copyright Clearance Center
When it comes to people, hiring talent is only the beginning. Organizations must also pay attention to organizational culture and structure because they carry the same level of importance in the delivery of successful digital transformation projects.
Companies must also pursue the right business strategy. It goes a long way in driving the digitization of internal as well as the growth of new business models.
A proper convergence of the people (with an excellent organizational structure and culture), a well-thought-out business strategy, and emerging and foundational technologies will facilitate the delivery of valuable digital products/services to the customers.
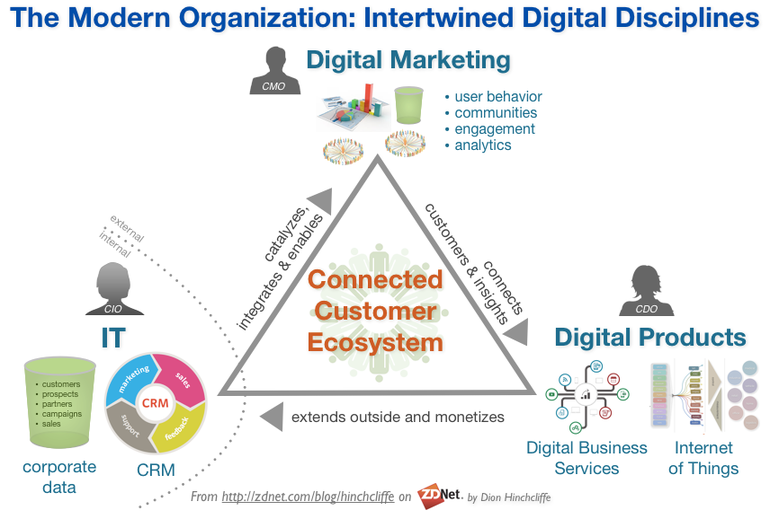
Image Source: Enterprise Regulars
The only time we can narrate digital transformation success stories is when companies can use created data effectively, by/through technology in a manner that triggers the dynamic occurrence of business change.
How Has Digital Transformation Helped Businesses?
The coming of digital transformation has encouraged businesses to take a step back and revisit all their activities. Organizations are re-evaluating their internal systems and customer interactions (both online and in-person).
Firms have found themselves looking for answers to big questions related to process changes capable of enabling improved decision-making, customer experiences accompanied by increased personalization and game-changing efficiencies.
Top Benefits of Digital Transformation
For your business to remain competitive in its industry and pretty much stay ahead of the competition, you need to operate in a digitized domain. By doing so, you will not only build long-term relationships with your customers but also enjoy a flurry of benefits that come with digital transformation.
Growth in technology has improved the interactions between companies and customers. Organizations can now offer better and consistent experiences in the fulfillment of customers’ needs.

Image Source: Marketing Week
Nowadays, one of the ways of ensuring satisfactory customer experiences is acting with speed. As a result, a firm that has successfully embraced digital transformation can engage and serve its customers faster than before.
More and more companies are adopting new technologies in an effort to remain competitive and grow. Employees, however, are left with no choice but to upgrade their skills to keep pace with the ever-changing technological environment.
This means that their knowledge also improves substantially, which translates to more agility and enhanced communication across all the company departments. The new skills and knowledge also lead to the delivery of quality work at all times.
What is more, knowledgeable and highly skilled employees are happier compared to those who don’t have a clue about the technological changes taking place in the world of business. To ensure the continuation of the same morale, invest in user training each time you introduce new technology in the workplace.
At the same time, encourage a culture where questions about the systems are always encouraged and responded to. This way, you will keep your workers interested in ensuring optimal utilization of new technologies, and consequently, improved customer service and profitability.
Digital transformation has facilitated the online collection of data. Firms can now monitor, collect and also analyze customer data thanks to the availability of reliable data analytics tools.
Decision-making has become a whole lot easier, faster and near-perfect. In the past, it was a bit difficult to study consumer habits and this made the enhancement of business strategies problematic.
Today, the scene has dramatically changed, with businesses gaining the ability to understand the habits of their target market over the internet.
Technology advancement has also immensely contributed to ever-changing consumer behaviors. For instance, you must have realized that the modern consumer doesn’t particularly like to wait. He or she loves to get things done instantly, and as such, only prefers to purchase from retailers that can deliver fast.
The introduction of digital transformation has enabled organizations to turn tangible products into digital products and, consequently, meet and exceed the expectations of their customers.
This achievement has contributed significantly to businesses’ ability to retain or even widen their client base. Such a digital transformation strategy will also help you gain an edge over your competitors.
Successful implementation of digital transformation facilitates positive changes in all aspects of your business. This, therefore, means that your revenue also gets to grow at an unimaginable rate.
Most importantly, when a business can improve customer experiences and engagements, leads almost always turn into conversions and ultimately customer loyalty. With time, loyal customers become brand ambassadors, and the rest, as they say, is history.
Undoubtedly, a properly executed digital transformation strategy opens new doors for businesses. It is one of the surest ways of making it big, even in a highly competitive market. Of the utmost importance is that you get it right!
So, how do you ensure the successful implementation of digital transformation in your business to reap optimal benefits?
Keys to Successful Digital Transformation
Talent and capabilities are among the aspects that experience changes during digital transformation. According to a new McKinsey global survey, about 70 percent of the respondents affirmed that the top teams of their organizations changed during digital transformation – with new leaders whose familiarity with digital technologies is unbeatable, joining the management team.
Such additions are among the keys to successful digital transformation. Of equal importance is the identification of transformation-specific roles such as individual- initiatives leaders and program management/transformation office leaders. These leaders must dedicate all their time to the change effort.
Leadership commitment is also key to the success of every digital transformation program. Personalities in crucial roles, namely senior positions and transformation-specific capacities, exhibit more level of involvement in digital transformation compared to before, and success is attainable.
The McKinsey survey also revealed that nearly a third of organizations go-ahead to employ a chief digital officer during digital transformation. The likelihood of these companies reporting the successful execution of digital transformation is 1.6 times higher compared to others.
Talent and skills development across the entire organization is one of the key contributors to successful digital transformation.
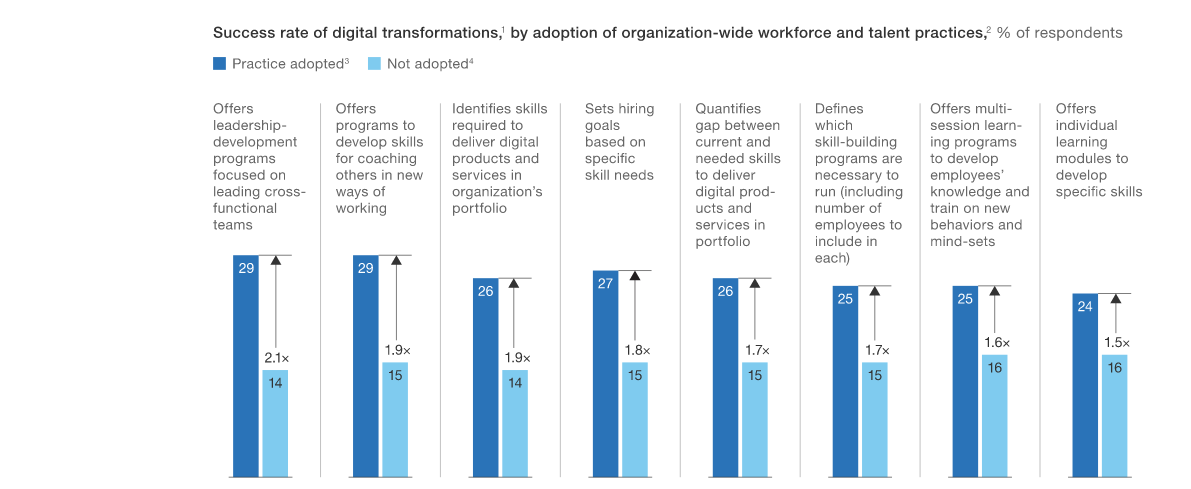
Image Source: McKinsey & Company
The first focus should be put on redefining the roles and responsibilities of the individuals in line with the digital transformation goals. The other aspect entails engaging the particular roles of integrators as well as technology-innovation managers.
These staffers help to bridge the possible gaps between the analog and digital areas of the business. Individuals in this role help to build powerful internal capabilities among fellow workers.
Integrators perform the critical role of translating and integrating new digital techniques and processes into traditional ways of doing business. They get this capability from the experience they have gathered over time and their understanding of the technical aspects and the benefits of digital technologies.
On the other hand, tech innovation managers have specialized technical skills and have been leading digital innovation projects within the firm.
The size of the budget a company is willing to allocate to talent and skills development is also a vital determinant of the level of success it can acquire in digital transformation.
Organizations with winning digital transformations have adequately funded budgets for digital talent. Digital talent doesn’t have to take up the biggest share of the company budget. However, investing in the right amount will significantly help to drive transformation success.
Companies that shy away from empowering their employees to work in new ways must prepare to handle a high digital transformation failure rate.
Digital transformation success stories are characterized by aspects such as behavioral and cultural changes. Employees need to be encouraged to embrace productive elements such as increased collaboration, customer centricity, and calculated risk-taking.
Utilize formal mechanisms to reinforce new behaviors and fresh ways of accomplishing tasks. Begin by devising practices associated with new ways of working like open work environments and continuous learning.
Employee engagement is equally essential in digital transformation. Allow your employees to have a say on possible areas for the adoption of digitization. By allowing them to give ideas about where digitization is the most important in business, you are more likely to report success in digital transformation.
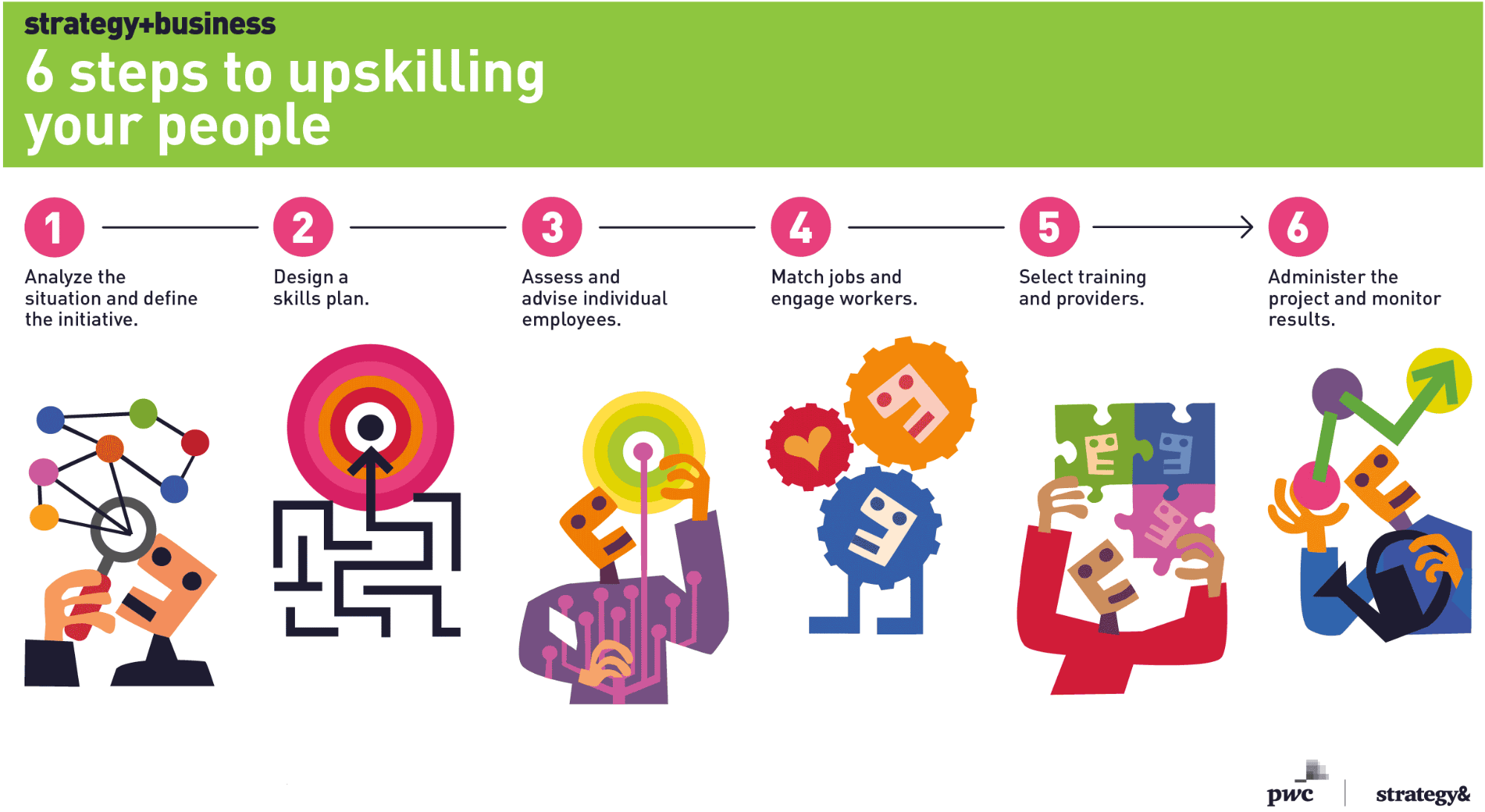
Image Source: Strategy + Business
Make sure that people who hold vital roles are instrumental in driving change. Note that success is dependent on senior leaders and all the people you engage in all the levels of transformation.
Top leadership and people in transformation-specific roles should encourage employees to challenge conventional ways of doing things. Employees are also likely to ensure transformation success where they are allowed to learn from the mistakes they make in the process of experimenting with new ideas.
Lastly, encourage the highest level of collaboration between departments. This can only happen if people in key roles are willing and ready to entertain collaboration.
Other keys to successful digital transformation include a continuous digital upgrade of everyday business tools and frequent communication using both traditional and digital methods.
If your digital transformation journey hasn’t been as successful as you had envisioned, critically look at the above five factors and determine where you’ve been missing the point. There are numerous other factors that you can consider to ensure the realization of transformation goals.
Let Us Now Look At the Post Digital Transformation World

In February 2019, Paul Daugherty, via Accenture, reminded players in the world of business about the coming of the post-digital transformation. He talked about the incredible speed at which technological change boldly sweeps across the industry.
Daugherty foresaw a shift from the digital era to a new reality – the post-digital period.
The rate at which organizations are adopting digital technologies is unprecedented. By the end of 2019, spending on digital transformation is expected to hit a whopping $1.25 trillion.
These efforts have led to digital technologies increasingly becoming a powerful driver of the core business operations, according to a survey conducted by Accenture in its 2019 report,
Seventy-nine percent of the over 6,600 IT and business executives who were interviewed said that digital technologies have gone beyond adoption silos and are now a crucial part of the technology foundation for their firms.
This leads us to the next important question.
Now that nearly all global organizations are done with their first transformation wave in becoming digital businesses…
What does the future hold?

The post-digital era is quickly approaching. Becoming digital is no longer about attaining a competitive advantage. Instead, it has become the new way of doing business.
What does this mean? With digital saturation in the picture and a level playing field, organizations will have to devise ways of dealing with the challenges related to ever-evolving and growing demands from their customers, partners, and the employees.
In this new world of digital transformation, successful companies will be those that, among other things, employ foundational apps and a new generation of innovations and technologies to stand out in the market place through the delivery of the best customer experience and in good time.
Before long, companies will move away from foundational apps. Individual departments will begin to use their domain-specific SaaS apps, which might include other record systems. This will stimulate the need to think about the automation of business processes throughout the company.
If this has to be actualized, then organizations must think in the line of linking two or more apps. No conversations will be held without the term “integration,” raring its head. This means that integration will automatically become mission-critical for companies to succeed.
While integration is a critical component in any automation strategy, the specific level of integration will differ significantly – depending on factors such as the things at stake, the costs involved, and the stage in which an organization is in its lifecycle.
The Integration Maturity Model
In which category does your company fall?
In this stage, the company’s primary focus is to establish a product-market fit. It, therefore, means that the business is yet to settle on a long term business process. Manual processes dominate the activities of the firm.
The organization lacks an integration strategy in place. Since integration hasn’t been acknowledged as a pain point or major need from the IT organization, integrations are mostly reactive with drive originating from individuals keen on solving the challenges they face on a need-basis. Every integration is manual, tailored, point to point, and is usually a one-off thing.
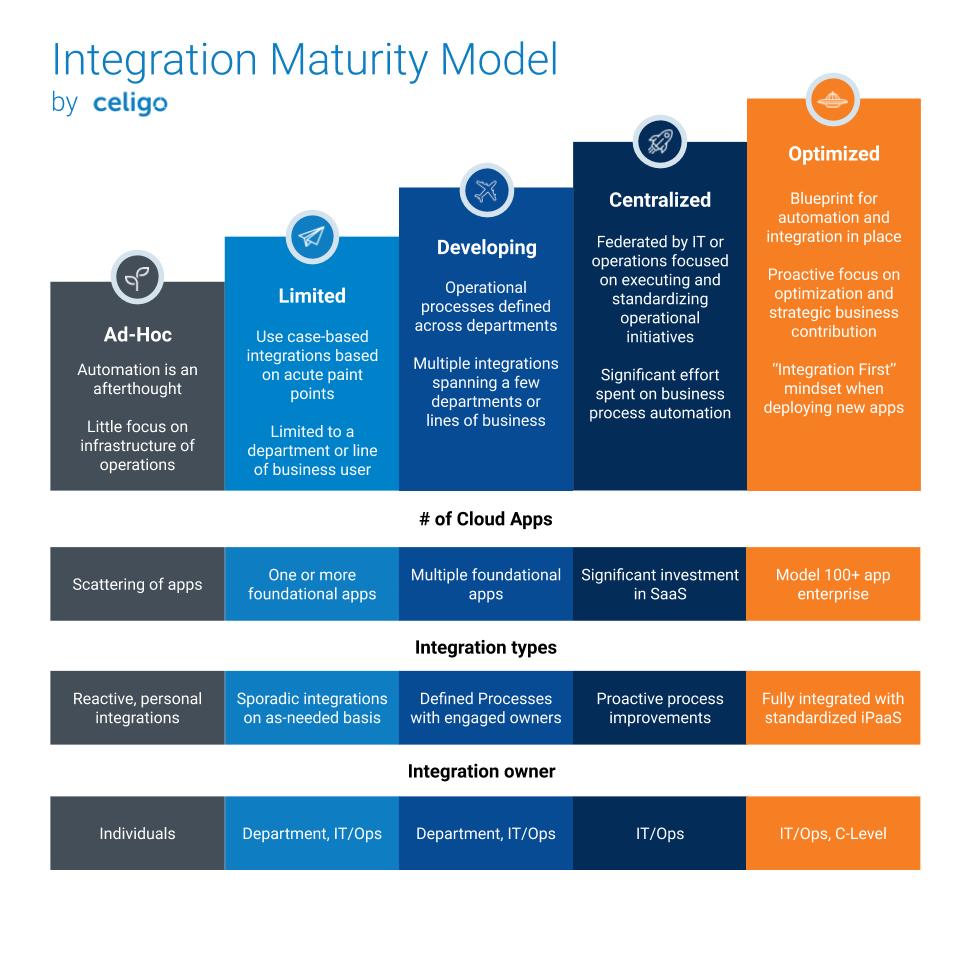
Image Source: Celigo
The users in the ad-hoc tier are IT professionals.
Although slowly, companies begin to grow and embrace additional SaaS apps. Even though operational efficiency gets the most attention, integrations are still reactive. Look at it this way: an app is needed, which gives birth to a pain point.
What follows is the rise of an immediate need that must be met instantly. Undoubtedly, the most typical reaction is to depend on vendor-built integrations, out-of-the-box integrations, and in worst-case scenarios, the deployment of direct API integrations with technical resources.
In a nutshell:
Companies in this stage have APIs published; they begin to realize that integration is a challenge; there are neither connectors nor endpoints and integrations are still tailored, and point-to-point. The users are IT professionals and developers.
A few developments are visible in this stage. The company is now working across multiple departments to get clear business processes. The implementation of foundational SaaS apps has happened, with more and more SaaS apps being adopted regularly. It is clear that the need for integration has grown considerably.
Unfortunately, the ad-hoc and native integrations that happened previously become problematic. The company must deal with the maintenance and compliance challenges as far as tracking and updating the SaaS apps is concerned. A higher sophistication of the business processes may demand the need for customizations, which, sadly, are mostly unsupported.
Thankfully, since companies in this tier have better-defined processes, they exhibit impressive proactiveness in the identification of operational issues and what is needed to address them. There isn’t a better time to consider adopting an integration platform to speed up the time spent on integrations and to reduce the corresponding maintenance costs.
At this point, the adoption of apps and integration needs of the firm is increasingly growing. As such, organizations in this tier have realized the benefits of dedicating resources towards IT tasked with the responsibility of building and owning integrations across the company departments.
The centralized set of resources accompanied by technical know-how is best suited for determining integration needs throughout the organization. They should be encouraged to enhance collaborations between different units. Increased partnerships will facilitate the delivery of solutions capable of automating business processes across the board.
The majority of companies in this lifecycle stage have an iPaaS, and both business and IT users can not only build but also maintain the integrations that meet their specific needs.
This is the highly sought after stage in the integration maturity model. You will know your company has reached this point if it has gone beyond the pain point model of integration.
If you are already seeing integration as a strategic advantage to get ahead proactively and take the business to the next level, then you’ve made it. How can you not achieve this goal while you already have an automation flywheel for optimizing business processes on an ongoing basis?
With fully standardized integration on an iPaaS and federation across functions, you’ve actualized your digital transformation strategy. Don’t stop, though. Ensure that the IT department continues to actively look for new ways through which the organization can achieve more with minimal resources.
Companies can use the integration maturity model to assess and enhance their integration competency. Do not be scared if your integration strategy tends to incline to the left. The most important thing is first to identify where you stand and then act towards entering and going beyond the upper tiers.